Appearance
vue3 部分知识点
toRefs, toRef
let person = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: 19
})
// 解构出来的name不是响应式的,因为响应式代理的是对象本身,解构赋值相当于把值 复制 出来了,脱离了响应式系统,修改name不会触发person.name改变。
let { name, age } = person
function changeName() {
name += '~'
}let { name } = toRefs(person)
console.log('name---', name) // ObjectRefImpl
function changeName() {
name.value += '~' // person.name 会改变
}
// or
let name = toRef(person, 'name')
console.log('name---', name) // ObjectRefImpl
function changeName() {
name.value += '~'
}computed
let num1 = ref(0)
let num2 = ref(0)
// let sum = computed(() => {
// return (parseFloat(num1.value) || 0) + (parseFloat(num2.value) || 0)
// })
// // computed 计算有缓存,只读
// function changeComputedValue() {
// sum.value = 222 // computed value is readonly
// }
let sum = computed({
get() {
return (parseFloat(num1.value) || 0) + (parseFloat(num2.value) || 0)
},
set(val) {
// console.log('value', val)
const [n1, n2] = val.split('-')
num1.value = n1
num2.value = n2
}
})
function changeComputedValue() {
sum.value = '8-9' // 触发 set 方法, num1,num2和sum都改变
}
watch
watch 可以监听:
- ref 定义的数据
- reactive 定义的数据
- 函数返回一个值(getter 函数)
- 一个包含上述内容的数组
ref 定义的基本类型
let val1 = ref(0)
const stopWatch = watch(val1, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
if (newValue >= 10) {
stopWatch() // 移除监听
}
})
function changeSum() {
val1.value += 1
}ref 定义的对象类型
let val2 = ref({
name: 0
})
// val2对象的地址值变化才能监听到;只改name监听不到
watch(val2, (newValue) => {
console.log('监听val2变化', newValue)
})
function changeVal2Name() {
// val2.value.name += '~' // 监听不到
val2.value = { name: 1 }
}优化:
let val2 = ref({
name: 0
})
watch(
val2,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
// val2.value.name += '~' => newValue, oldValue 都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象 (true)
console.log('监听val2变化', newValue, oldValue, newValue === oldValue)
// val2.value = { name: 1 } => newValue是新值,oldValue是旧值,不是一个对象了 (false)
},
{ deep: true } // 需要开启deep才能监听到ref定义的对象属性变化
// immediate: true
)
function changeVal2Name() {
val2.value.name += '~'
// val2.value = { name: 1 }
}reactive 定义的对象类型
let val3 = reactive({
name: 0
})
// reactive定义的对象类型监听时默认开启了深度监听deep,且无法关闭
watch(val3, (newValue) => {
console.log('监听val3变化', newValue)
})
function changeVal3Name() { // reactive定义的数据不能直接修改,可以通过Object.assign()方法修改
// val3.name = 888
Object.assign(val3, { name: 999 })
}一个函数返回一个值(getter 函数)
监听响应式对象某个属性,且该属性是基本类型:
let val3 = reactive({
name: 0,
age: 18
})
watch(
() => val3.name,
(newValue) => {
console.log('监听val3.name变化', newValue)
}
)
function changeVal3Name() {
val3.name = 888
}监听响应式对象某个属性,且该属性是对象类型:
这种写法兼听不到对象整体改变:
let val3 = reactive({
name: 0,
age: 18,
obj: {
count: 1
}
})
watch(val3.obj, (newValue) => {
console.log('监听val3.obj变化', newValue)
})
function changeVal3Name() {
val3.obj.count = 2
// val3.obj = { count: 3 } // 整体改变,这个监听obj监听不到
}这种写法监听不到属性改变:
let val3 = reactive({
name: 0,
age: 18,
obj: {
count: 1
}
})
watch(
() => val3.obj,
(newValue) => {
console.log('监听val3.obj变化', newValue)
}
)
function changeVal3Name() {
// val3.obj.count = 2 // 这个写法属性改变监听不到
val3.obj = { count: 3 }
}优化:
就采用这种写法:
let val3 = reactive({
name: 0,
age: 18,
obj: {
count: 1
}
})
watch(
() => val3.obj,
(newValue) => {
console.log('监听val3.obj变化', newValue)
},
{
deep: true
}
)
function changeVal3Name() {
// val3.obj.count = 2 // 2种写法都能监听到
val3.obj = { count: 3 }
}监听一个包含上述内容的数组
watch(
[val2, () => val3.obj],
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('监听', newValue, oldValue)
},
{
deep: true
}
)watchEffect
watchEffect 响应式地追踪其依赖,并在依赖更改时重新执行该函数
watchEffect(() => {
console.log('一上来就执行一次watchEffect')
// num1、num2 任何一个发生变化都会执行
if (num1.value >= 10 || num2.value >= 10) {
console.log('超过10')
}
})标签 ref 属性
用在 html 标签上:
<template>
<div>
<div ref="refEle">dom</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
const refEle = ref(null)
onMounted(() => {
console.log(refEle.value)
})
</script>用在子组件上:
如果不用 defineExpose 暴露出去,父组件无法访问子组件内容
// 父组件
<CommonHeader ref="compRef" />
let compRef = ref()
onMounted(() => {
console.log(compRef.value, compRef.value.keywords)
...
}
// 子组件
import { ref, defineExpose } from 'vue'
let keywords = ref('test')
defineExpose({ keywords })组件 props
父组件:
<template>
<Person a="哈哈" :list="personList" />
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import Person from './components/Person.vue'
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import { type Persons } from './types'
// const personList: Persons = reactive([
// {
// id: '1',
// name: 'xhh',
// age: 19,
// },
// {
// id: '2',
// name: 'lb',
// age: 20,
// },
// ])
// or 泛型
const personList = reactive<Persons>([
{
id: '1',
name: 'xhh',
age: 19,
},
{
id: '2',
name: 'lb',
age: 20,
},
])
</script>src/types/index.ts:
// 接口
export interface PersonInter {
id: string
name: string
age: number
}
// 自定义类型
// export type Persons = Array<PersonInter>
// or
export type Persons = PersonInter[]子组件:
const x = defineProps(['a', 'list'])
console.log(x, x.a, x.list)
加上类型校验:
import { type Persons } from '@/types'
defineProps<{ list: Persons }>()类型校验+可选传参:
父组件不传 list 也可以
import { type Persons } from '@/types'
defineProps<{ list?: Persons }>()类型校验+可选传参+默认值:
// [@vue/compiler-sfc] `withDefaults` is a compiler macro and no longer needs to be imported.
// import { withDefaults } from 'vue'
import { type Persons } from '@/types'
withDefaults(defineProps<{ list?: Persons }>(), {
list: () => [
{
id: '2-2',
name: 'haha',
age: 24,
},
],
})Router
创建路由:
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(import.meta.env.BASE_URL),
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
name: 'login',
meta: {
title: '登录'
},
component: () => import('../views/login')
},
...
],
scrollBehavior: () => {
// 新开页面滚动条回到顶部
return { top: 0 }
}
})
export default router挂载路由:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import router from './router'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(router)渲染出匹配到的路由:
<RouterView :key="$route.fullPath" />接收参数
import { useRouter, useRoute } from 'vue-router'
const router = useRouter()
const route = useRoute()
console.log('route:', route)
console.log('router.currentRoute.value:', router.currentRoute.value)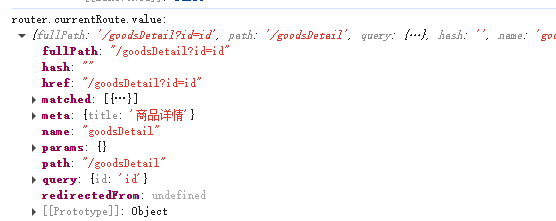
路由规则的 props 配置
{
path: '/waterfallPage',
name: 'waterfallPage',
meta: {
title: '瀑布流'
},
component: () => import('../views/waterfallPage'),
children: [
// 嵌套路由 /waterfallPage/waterfall
{
path: 'waterfall/:a?/:b?',
name: 'waterfall',
meta: {
title: '瀑布流子页面'
},
component: () => import('../views/waterfall'),
// <waterfall a="" b="" />
// props: true // 写法一、将路由收到的所有params参数作为props传递给路由组件
props(route) {
// 写法二、自己决定将什么作为props传递给路由组件
// return route.query
return route.params
}
// props: {
// // 写法三
// a: 100
// }
}
]
}页面接收:
defineProps(['a', 'b'])replace
<RouterLink replace to="/goodsDetail?id=2">goodsDetail</RouterLink>
router.replace({
name: 'confirmOrder'
})重定向
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/home'
}pinia
引入 pinia
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
const pinia = createPinia()
app.use(pinia)创建 store(目录 src/store):
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// 官方推荐命名格式
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state() {
// 存储数据
return {
count: 0
}
},
getters: {
double: (state) => state.count * 2
},
actions: {
increment(value) {
this.count += value
}
}
})使用 store:
import { useCounterStore } from '@/store/counter'
const counter = useCounterStore()
console.log('获取 store count:', counter.count, counter.$state.count)
function addShopCart() {
// pinia
// counter.count += 1
// or
counter.$patch({
count: counter.count + 1
})
// or
// counter.$patch((state) => {
// state.count = counter.count + 1
// })
// or
// counter.increment(1)
}持久化存储
localStorage 或 pinia-plugin-persistedstate 插件
storeToRefs
// 这种写法不是响应式数据,修改了count页面上的countValue不更新
let countValue = counter.count
console.log('--toRefs(counter)--', toRefs(counter)) // 不建议这么写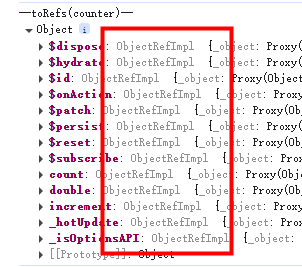
// storeToRefs 获取响应式数据,只会关注store中的数组,不会对方法进行ref包裹
let countValue = storeToRefs(counter).count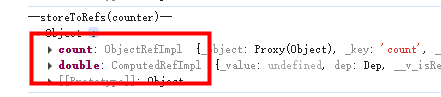
$subscribe
counter.$subscribe((mutate, state) => {
// store中的数据发生了变化
console.log('$subscribe:', mutate, state.count)
})组合式写法
// store 组合式写法
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(localStorage.getItem('storeCount') || 0)
const double = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment(value) {
count.value += value
}
return { count, double, increment }
})
counter.$subscribe((mutate, state) => {
// store中的数据发生了变化
localStorage.setItem('storeCount', state.count)
console.log('$subscribe:', mutate, state.count)
})v-model
用在 input 等标签上
<input v-model="keyword" />
// or
<input
:value="keyword"
@input="keyword = (<HTMLInputElement>$event.target).value"
placeholder="请输入"
/>用在自定义组件上
// 父组件
keyword: {{ keyword }}
<XhhInput v-model="keyword" />
// 等同于
<XhhInput :modelValue="keyword" @update:modelValue="keyword = $event" />
<!-- 对于自定义事件,$event就是触发事件时所传递的数据,不能 .target -->
// 子组件
<template>
<input
:value="modelValue"
@input="emit('update:modelValue', (<HTMLInputElement>$event.target).value)"
placeholder="请输入"
/>
<!-- 原生事件,$event就是事件对象,$event.target就是input元素 -->
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
defineProps(['modelValue'])
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])
</script>或 子组件使用 v-model 绑定传来的变量:
<template>
<input v-model="newValue" placeholder="请输入" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
const props = defineProps(['modelValue'])
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])
const newValue = computed({
get() {
return props.modelValue
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', val)
},
})
</script>或 Vue3.4+ defineModel:
<template>
<input v-model="model" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
const model = defineModel()
</script>v-model 修改绑定的变量
<XhhInput v-model:modelValueOther="keyword" />
<XhhInput v-model:modelValueOther="keyword" v-model:xyz="abc" />
<template>
<input
:value="modelValueOther"
@input="emit('update:modelValueOther', (<HTMLInputElement>$event.target).value)"
placeholder="请输入"
/>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
defineProps(['modelValueOther'])
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValueOther'])
</script>插槽
默认插槽
在子组件
<slot></slot>
// 等同于
<slot name="default"></slot>具名插槽
<Person>
<template v-slot:title>
<div>this is title</div>
</template>
<template #header>
<div>this is header</div>
</template>
</Person>
<div>
<div>Person组件:</div>
<slot name="header"></slot>
<slot name="title"></slot>
</div>作用域插槽
<Person>
<template v-slot="params">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in params.listP" :key="index">
{{ item.title }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
</Person>
<Person>
<template v-slot="{ listP }">
<ol>
<li v-for="(item, index) in listP" :key="index">
{{ item.title }}
</li>
</ol>
</template>
</Person>
// Person.vue
<slot :listP="list"></slot>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const list = reactive([
{
title: '标题1',
},
{
title: '标题2',
},
{
title: '标题3',
},
{
title: '标题4',
},
])和具名插槽结合在一起
<template v-slot:listcon="{ listP }">
// or
<template #listcon="{ listP }">
// Person.vue
<slot name="listcon" :listP="list"></slot>shallowRef, shallowReactive
浅代理,只代理对象属性,不代理对象属性的属性
import { shallowRef } from 'vue'
const sum = shallowRef(0)
const person = shallowRef({
// 只能处理第一层的响应式
name: 'zs',
age: 29,
})
function changeSum() {
sum.value += 1
}
function changePersonName() { // ref定义的生效,shallowRef定义的修改不生效
person.value.name = 'ls'
}
function changePersonAge() { // ref定义的生效,shallowRef定义的修改不生效
person.value.age += 1
}
function changePerson() {
person.value = {
name: 'new name',
age: 99,
}
}import { shallowReactive } from 'vue'
const person = shallowReactive({
// 只能处理第一层的响应式
name: 'zs',
inner: {
age: 18,
},
})
function changePersonName() {
person.name = 'ls'
}
function changePersonAge() { // 不生效
person.inner.age += 1
}readonly, shallowReadonly
readonly 只读,不可修改
sum 可以改,改了 sum2 也跟着变; 但是 sum2 无法修改,数据保护
const sum = ref(0)
const sum2 = readonly(sum)shallowReadonly: 只作用于对象的顶层属性
const person = reactive({
name: 'zs',
inner: {
age: 18,
},
})
// person2的name不能改,person2.inner.age可以改
const person2 = shallowReadonly(person)toRaw, markRaw
toRaw: 获取响应式对象的原始对象,返回的对象不再响应式
let newPerson = toRaw(person)markRaw: 标记对象,使其永远不会成为响应式对象
import { reactive, markRaw } from 'vue'
const person = markRaw({ // 不是响应式
name: 'zs',
age: 18,
})
const person2 = reactive(person) // 不会成为响应式使用场景: 为了防止误把第三方库变为响应式对象
import mockjs from 'mockjs'
let mockJs = markRaw(mockjs)customRef
作用:创建一个自定义的 ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行逻辑控制。
使用 Vue 提供的 ref 定义的响应式数据,数据一变,页面立即更新。如果想过几秒再更新页面,ref 就做不到了。
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<input type="text" v-model="msg" placeholder="请输入" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { customRef } from 'vue'
let initialValue = ''
let timer: number
const msg = customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
get() {
track() // 告诉Vue追踪这个值,一旦msg变化就更新页面
return initialValue
},
set(newValue) {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
initialValue = newValue
trigger() // 通知vue数据msg变化了
}, 1000)
},
}
})
</script>封装优化:
useMsgRef.ts:
import { customRef } from 'vue'
export default function (initialValue: string, delay: number) {
let timer: number
const msg = customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
get() {
track() // 告诉Vue追踪这个值,一旦msg变化就更新页面
return initialValue
},
set(newValue) {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
initialValue = newValue
trigger() // 通知vue数据msg变化了
}, delay)
},
}
})
return {
msg,
}
}import useMsgRef from './useMsgRef'
const { msg } = useMsgRef('Hello', 1000)Teleport
父组件:
<div class="outer">
<img src="https://test/1.jpg" />
<Modal />
</div>
.outer {
background-color: #ddd;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
filter: saturate(200%);
}当父元素(如 body 或 div)开启 filter 效果时,CSS 会为该元素创建一个新的包含块。此时,使用 position: fixed 样式的元素的定位基准会从浏览器视窗(viewport)切换到该父元素,即子组件 fixed 会相对于父元素进行定位。
子组件 Modal:
为了使该组件还是相对于浏览器定位,需要使用 Teleport 组件。
<template>
<button @click="isShow = true">展示弹框</button>
<Teleport to="body">
<div v-if="isShow" class="modal">
<div>modal</div>
<button @click="isShow = false">关闭弹框</button>
</div>
</Teleport>
</template>
Suspense
子组件:
<script setup>
...
import axios from 'axios'
let data = await axios.get('https://www.test.shop/home')
console.log('data--', data.data.title)父组件:
<!-- <CommonHeader ref="compRef" /> -->
<Suspense>
<template #default>
<CommonHeader ref="compRef" />
</template>
<template v-slot:fallback>
<h3>加载中...</h3>
</template>
</Suspense>全局 API 转移到应用对象
- app.component
- app.config
- app.directive
- app.mount
- app.unmount
- app.use